Third-generation common rail with piezoelectric inline injectors

Conventional Common Rail system a magnetic coil controls the injector. A piston rod transmits the hydraulic force required to open or close the injector to the nozzle needle. In May 2003 series production began of Bosch’s third-generation Common Rail, in which the injector actuators consist of piezo crystals. Piezo crystals have the property of expanding in an electrical field.
The piezoelectric actuator is a package of several hundred very small, thin crystals. The piezo actuator switches in less than ten-thousandths of a second – less than half the time required by a magnetic switch. To exploit this property Bosch has integrated the actuator into the injector body.
In the inline injector, the movement of the piezo package is transferred to the rapid-switch nozzle needle without friction, as there are no mechanical components. The advantages over magnetic and existing conventional piezo injectors lie in a more precise dosing and improved atomization of the injected fuel mixture within the combustion chamber.
The higher switching speed of the injector means that the intervals between the individual fuel injections can be reduced, giving a more flexible control of the injection process. The result is that diesel engines become even quieter, more fuel-efficient, cleaner, and more powerful. With the in-line injector, the return flow of fuel not required for injection is very small. This allowed engineers to further reduce the delivery rate, and thus the energy requirement, of the high-pressure pump.
Improvements to the Unit-Injector System
Bosch’s Unit-Injector System (UIS) has the highest current injection pressure of any system at 2050 bar. At the moment this system is exclusively manufactured for passenger cars produced by VW. The very high injection pressures result, among other things, in low particulate emissions. This meant that some vehicles fitted with UIS were the first to meet the Euro 4 emission criteria. Bosch is presently working on further development of the UIS. A Coaxial Variable Nozzle will make the engines both quieter and cleaner, and further increase available engine performance.
Exhaust emission treatment
In Bosch’s approach to the further lowering of diesel engine emissions, the focus is primarily on internal engine improvements; improved fuel combustion prevents, as far as possible, the formation of pollutants and also reduces fuel consumption.
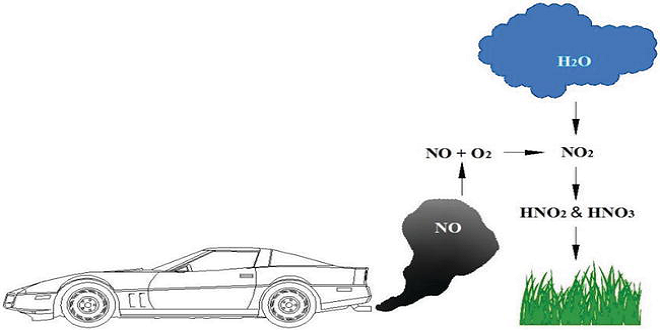
In this respect, automobile manufacturers and their component suppliers have already achieved a great deal. A number of vehicles with a maximum permissible overall weight of between 1600–1800 kg, and in some cases more than this, will come within the Euro 4 thresholds even without any exhaust treatment system.
Diesel particulate filters
If the injection system and the particulate filter are working optimally together, exhaust emission values can be further improved. Bosch, therefore, is likely to begin mass production of diesel particulate filters in late 2005. A final decision on this project is pending. The particulate filter from Bosch is made of sintered metal and lasts considerably longer than current ceramic models, since its special structure
offers a high storage capacity for oil and additive combustion residues.
Last word
The filter is designed in such a way that the filtered particulates are very evenly deposited, allowing the condition of the filter to be identified more reliably and its regeneration controlled far better than with other solutions. The Bosch diesel particulate filter is designed to last as long as the vehicle itself.